Last Updated: 27 August 2025 | Provide Feedback
Introduction
Welcome to the George Mason University Libraries tutorial, Find Sources FAST! In this tutorial, you will explore how to broaden your search results through citation mining to quickly find additional sources related to your research topic. Citation mining is a research technique that utilizes the sources you've already found to discover more sources relevant to your topic.
Citation Mining
Citation mining is a great way to locate more sources on a topic, examine the impact of a source, and track the scholarly conversation surrounding a particular research idea. Imagine a source as a seed, its bibliography (list of references, works cited, etc.) as the roots, and any works that have cited your source as the sprout.
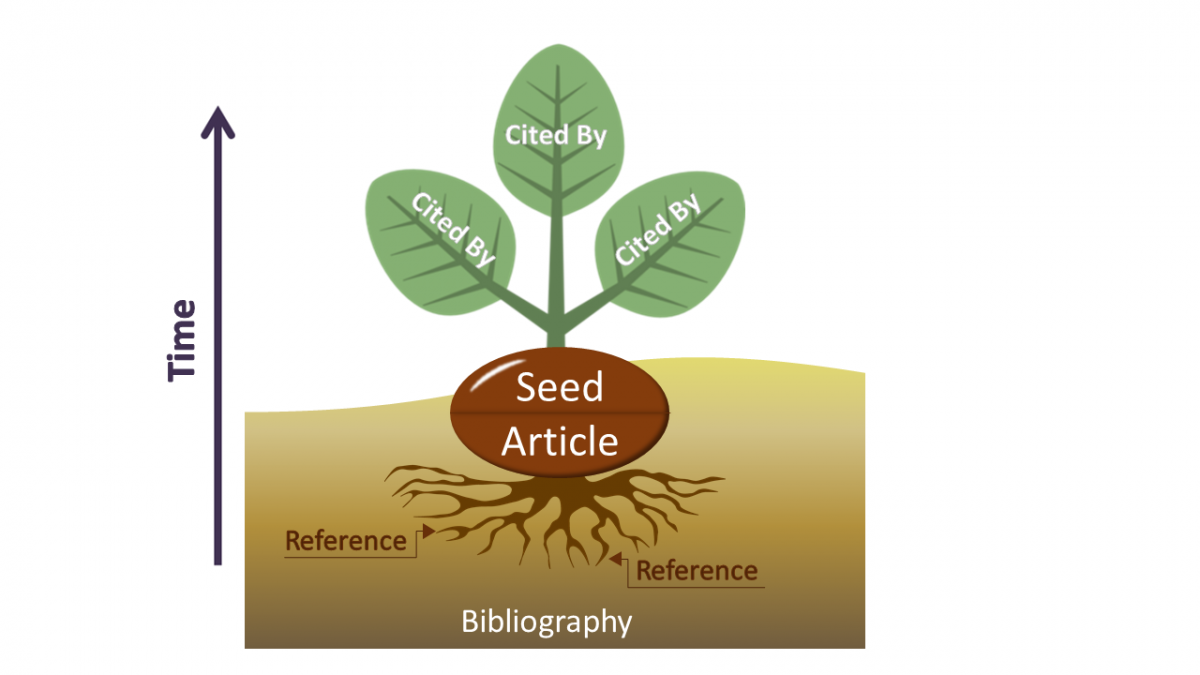
Once you've found your seed you can employ the following citation mining methods:
Backward citation mining - Investigate roots by examining the sources within the bibliography of the seed article
This can help you:
- Find other sources to include in your research
- Explore how a topic has changed over time
- Discover theories, constructs, and models used in research
- Identify experts, organizations, and/or institutions associated with the research topic
*Tip: While reading your source article, take notes of specific ideas, texts, and authors that relate to your research question. This will help you identify the most relevant sources within the articles bibliography or reference list.Forward citation mining - Conduct a citation search to discover what works may have sprouted from the seed article
Backward citation mining is extremely useful for gathering more background knowledge about your topic; however, some sources found through this method can be older or outdated. Forward citation mining (also known as cited reference searching) helps you discover useful and relevant sources that cite your original article. This will help you find newer research that builds upon your seed article. To conduct forward citation mining you have to use a tool provided in some databases and search engines. This tool will return other sources that cite your seed article. A few examples of resources with forward citation mining tools are:
- PubMed
- Web of Science
- Google Scholar
- Mason Search
- And more!
It is important to note that citation mining tools have limitations and don't always return an exhaustive list of all resources that exist. If you are getting limited results in one tool, try using another one to mine your seed article! To see if a database you are using has a forward citation mining tool, look around for options that say cited references, cited by, or that use similar language.
Related item mining - Compare bibliographies of similar seeds in the nearby soil to find similar works
Related item mining is useful for broadening your perspective on your research topic. This technique can help you find related research, counter-arguments, and new information on your topic. There are many different ways to look for items related to your seed article, including:
- Search for other articles written by the same author(s)
- Look for other items in the same publication
- Use the built in "related articles" feature used in many databases and Google Scholar
Just like forward citation mining tools, related item mining tools can be found in multiple databases and can look and function differently from site to site. Look for language including related articles, browse similar content, etc. when exploring a database to find similar tools. It is important to learn and explore multiple resources to be exposed to a full breadth of results and to optimize your search strategy.
Let's Practice!
Watch the video below to follow an example using the three citation mining techniques in Web of Science. To access Web of Science begin on the libraries' homepage, click on the blue Databases button beneath the Mason Search bar, and either browse under W or use the search box to find Web of Science: Core Collection. Despite its name, Web of Science has articles from all kinds of different topics, not just science topics, so it's a great resource for most research projects.
Do a survey and earn prizes
Complete this survey on the Finding Sources Fast! instructional guide to help the libraries improve our content to create more helpful learning objects. You'll be automatically eligible for a prize after the 1st, 6th, and 11th feedback forms you complete, and entered into a raffle for every feedback form you complete. Raffle prizes are stuffed backpacks of school supplies, a GMU Stanley cup, or a GMU hoodie/sweatshirt! The deadline to complete the survey is Sunday, March 15, 2026.
For a full list of tutorials with this prize opportunity, see the Tutorial Assessment Project page. Reach out to Elise Pino at emertz@gmu.edu with any questions or issues.
Get Help
For other questions or if you need more help try Ask a Librarian or explore the subject guide for your discipline. Use the button below to download an accessible, printable PDF of this tutorial.
![]() Find Sources FAST! by The Teaching & Learning Team is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Find Sources FAST! by The Teaching & Learning Team is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

