Introduction
Journal Citation Reports (JCR) is a tool that keeps track of the numbers of citations to articles published in top-tier scholarly journals in the hard and social sciences. You can use the median impact factor of all journals in a particular discipline reported in JCR as a baseline for comparing the impact factors of specific journals in that discipline.
What is impact factor?
Impact factor is a way of measuring the number of citations articles in a given academic journal receive on average. It is calculated by dividing the number of article citations by the total number of articles that could be cited from a particular journal. It is used as an indicator of the importance of a journal in a field, with journals with higher impact factors being more important.
What is the median impact factor?
The median impact factor is a number that helps you understand the "middle" impact factor of indexed journals in a field. Half of the journals in a discipline or subfield will be above the median impact factor, while half of the journals will be below this figure.
Why find the median impact factor?
Especially when you are first familiarizing yourself with a field or discipline, you will not know whether or not the articles you are finding were published in reputable, high-impact journals. JCR enables you to make some quick determinations that will help you understand this scholarly context. While the measures of influence reported by JCR are no substitute for familiarity and experience with a field, they can help you begin to orient yourself in relation to the field.
-
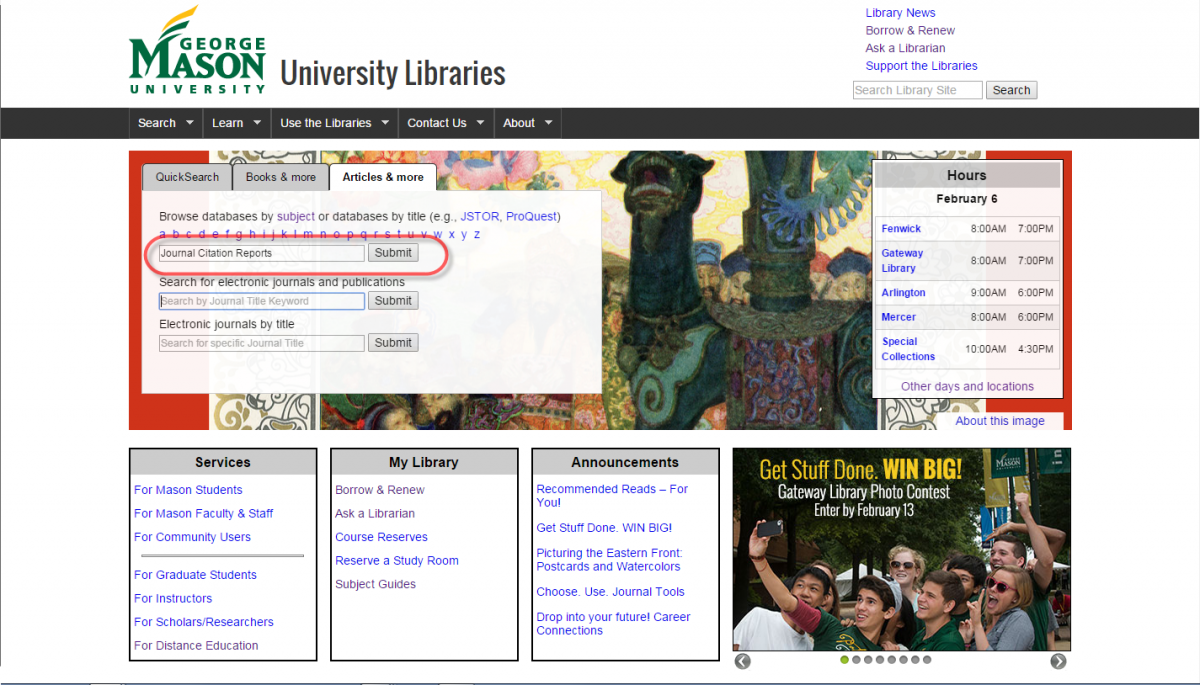
Locate JCR on the library website. Simply search for "Journal Citation Reports" in the Search Database Titles & Descriptions field on the Articles & more tab.
-
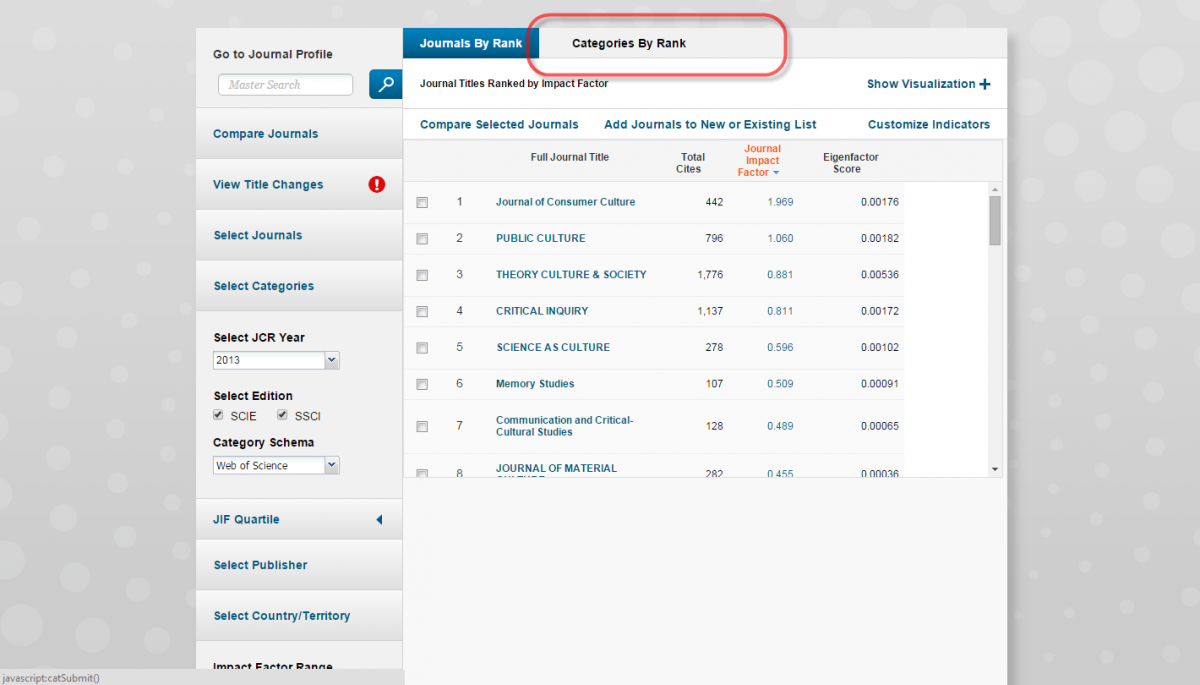
Select the "Categories by Rank" tab. This will list all of the indexed categories.
-
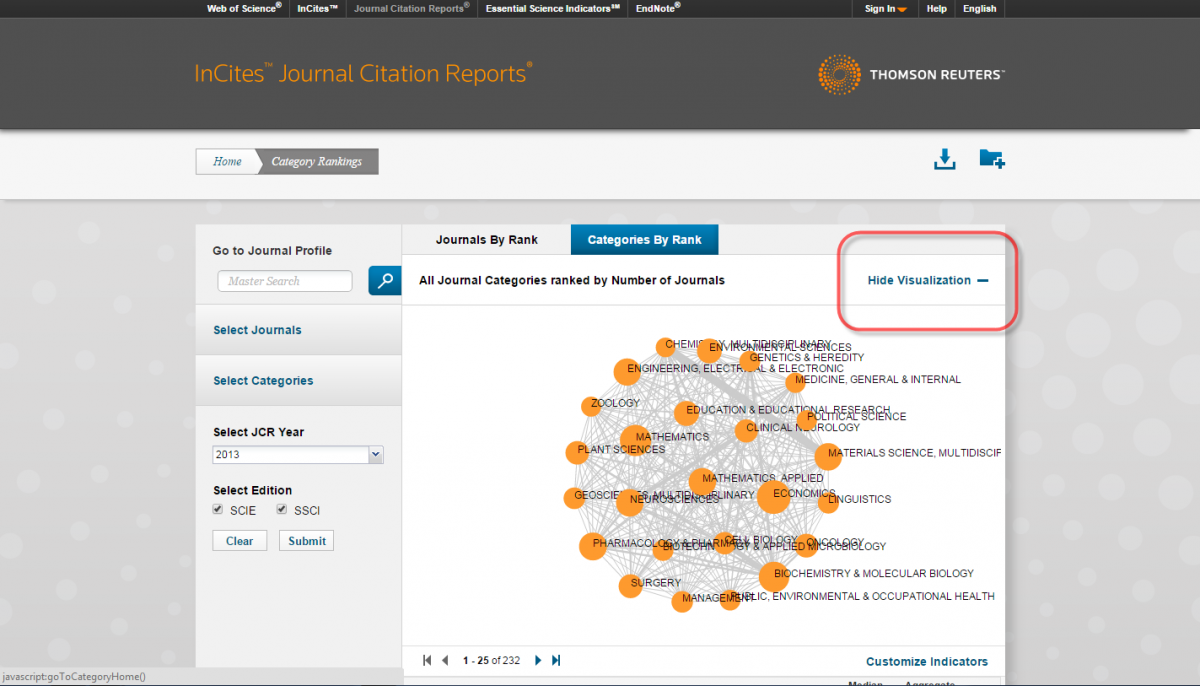
Click the "Hide Visualization" link. This will hide the web-like visualization of sources. Occasionally, the visualization will be hidden by default. If this is the case, you will see a "Show Visualization" link and you will need not take any action.
-
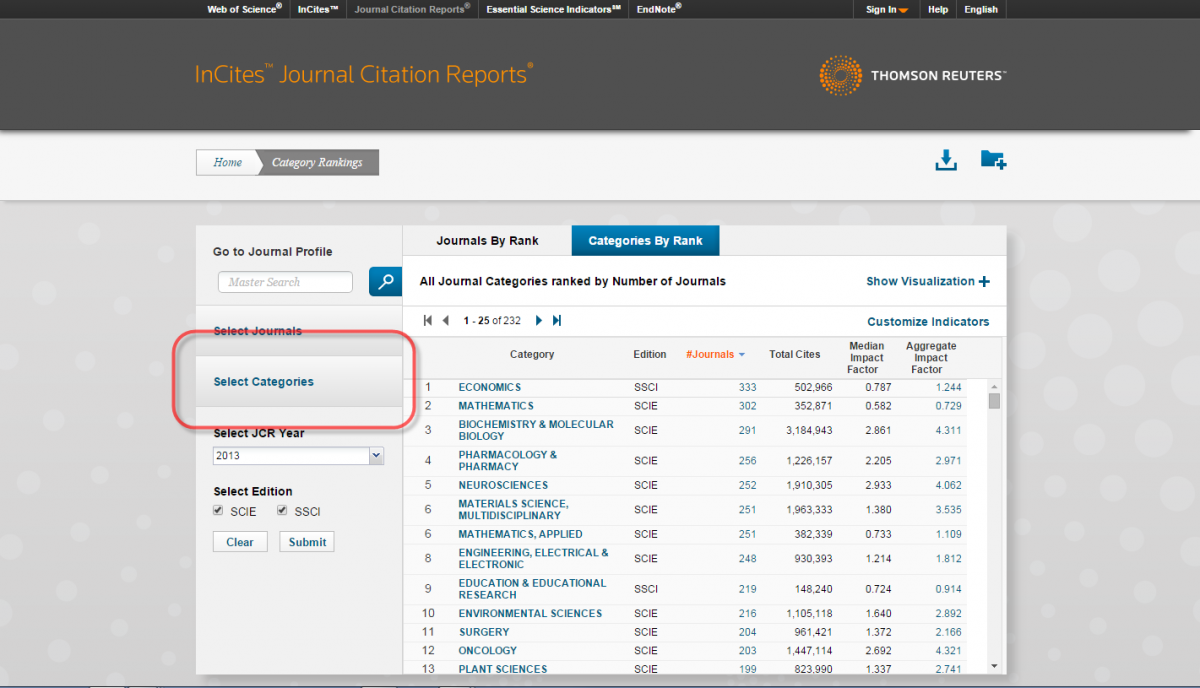
Click the "Select Categories" link and choose the disciplines or subfields that you are most interested in. The median impact factors in highly specialized subfields and interdisciplinary areas of study often differ from those in the larger disciplines. In order to get a more complete view of the field, select a field as well as relevant subfields or interdisciplinary fields.
-
Usually, you will leave the year set to the most current year. You may use the other years to learn about the historical impact factor of a journal.
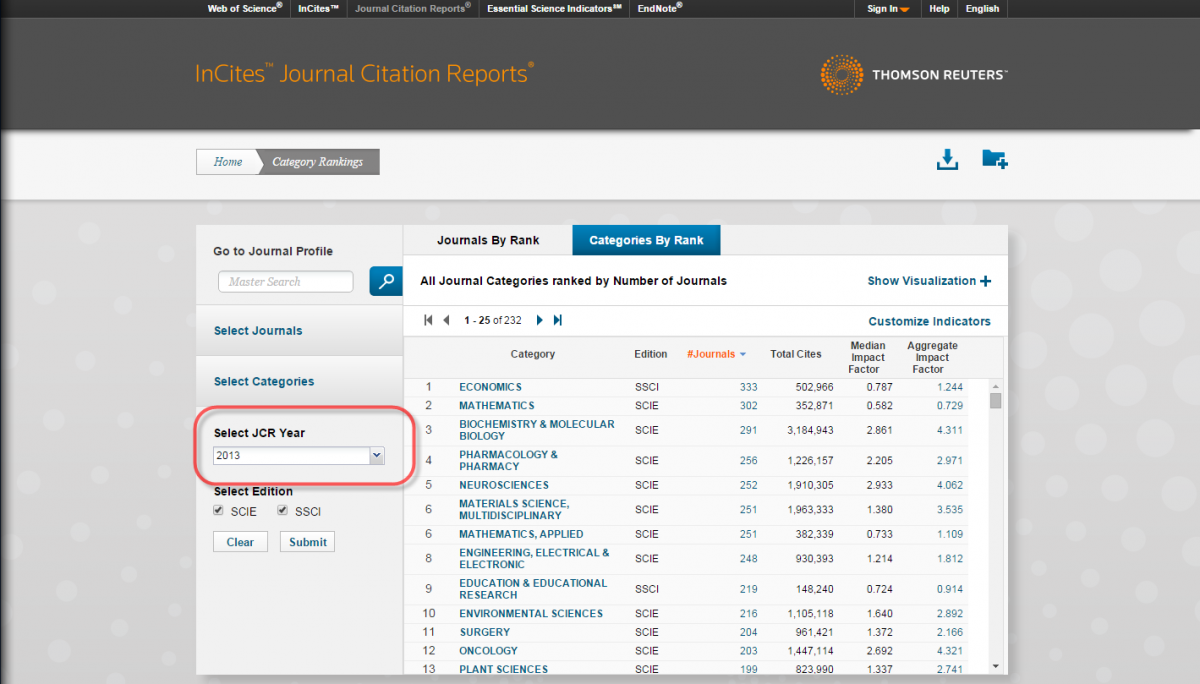
-
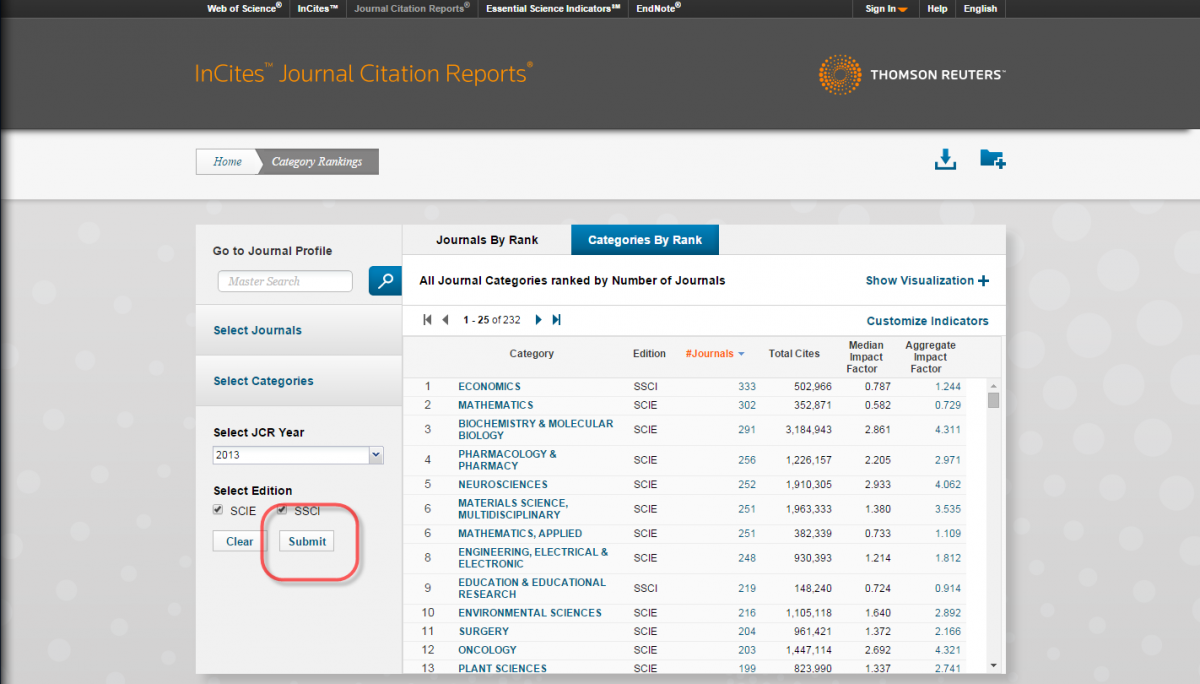
Click "Submit."
-
If you selected more than one category, Journal Citation Reports will rank them. Since different subfields have differing citation practices, this ranking is not particularly useful when trying to understand the influence and importance of a particular periodical.
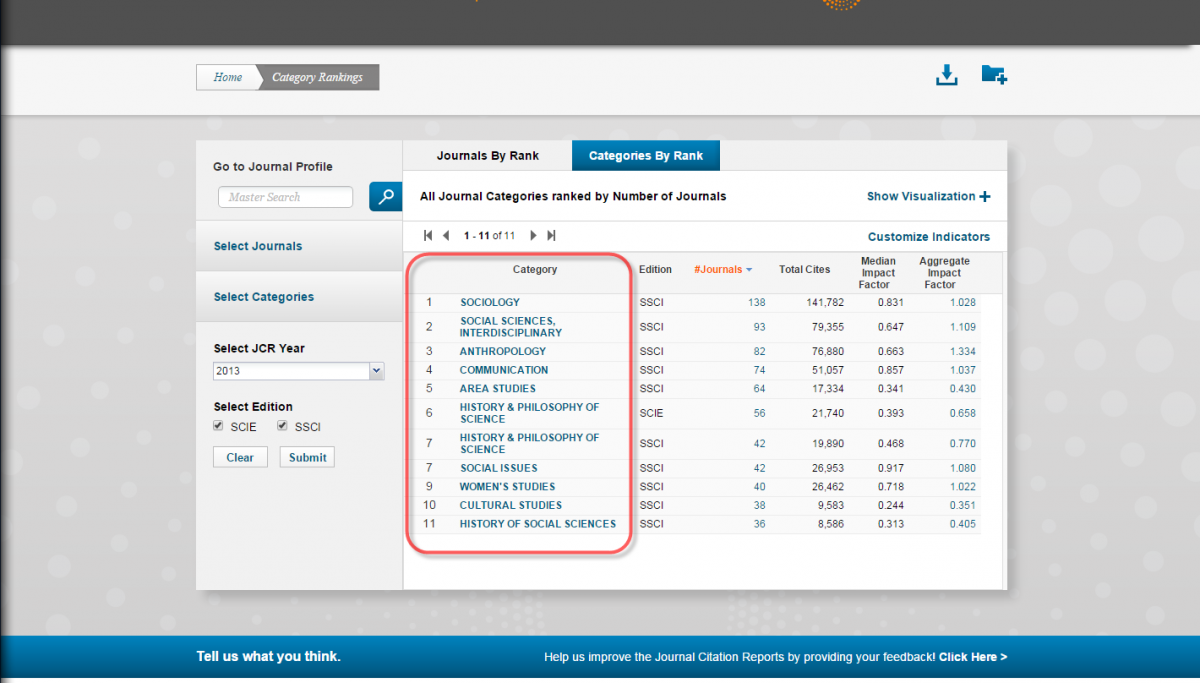
-
Write down the median impact factors in these fields and compare them to the impact factors of the journals you are investigating.
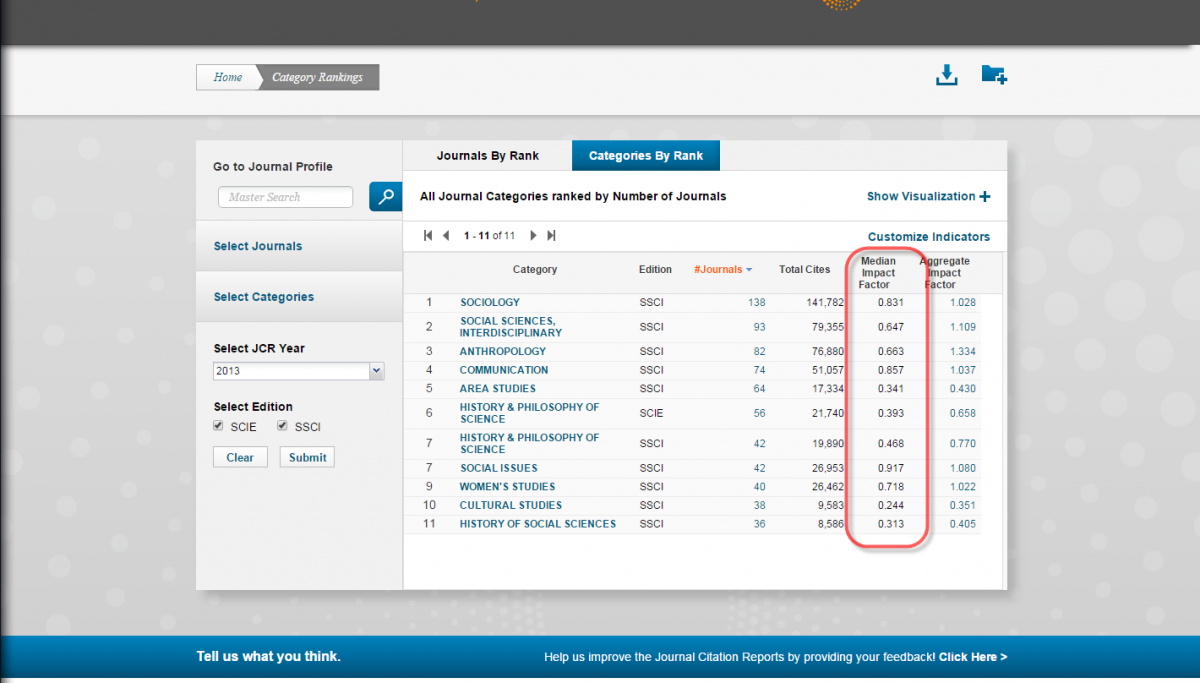
-
If the impact factor of a journal is lower than the median impact factor in the discipline, subfield, or interdisciplinary field it serves, this may mean that it less important or influential than most of the other journals serving that scholarly community.
Words of Caution
Citation metrics are imperfect. The best way to evaluate importance is through experience and familiarity with a field. Also be aware that citation behaviors differ substantially between subfields and may not be particularly important in some areas of study.
Ultimately, when researching, the most important thing to figure out is whether articles make substantial contributions to the scholarly conversations relevant to your research question.
Additional Questions and Help
If you have trouble or questions about the citation metrics, ask a librarian.

Median Impact Factor in a Discipline
is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
